- +91-8305 331 806
- thegastroliverclinic@gmail.com
- Avanti Vihar, Raipur
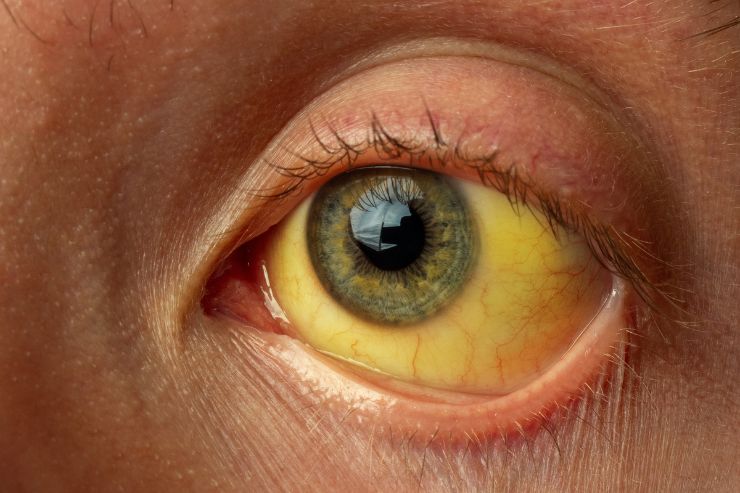
Jaundice is a condition characterized by yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes due to excess bilirubin in the blood. It can be caused by various underlying medical conditions affecting the liver, such as viral hepatitis, alcoholic liver disease, or bile duct obstruction. Effective treatment aims to address the underlying cause, reduce bilirubin levels, and alleviate symptoms.
Jaundice is a condition in which the skin, sclera (whites of the eyes) and mucous membranes turn yellow. This yellow color is caused by a high level of bilirubin, a yellow-orange bile pigment. Bile is fluid secreted by the liver. Bilirubin is formed from the breakdown of red blood cells.
See a doctor right away if you think you have jaundice. It could be a symptom of a liver, blood, or gallbladder problem.
Addressing the Underlying Cause: Treatment focuses on treating the specific condition causing jaundice. For example, antiviral medications are prescribed for hepatitis infections, and procedures may be performed to remove bile duct obstructions.
Symptomatic Relief: Patients may experience itching associated with jaundice. Medications or topical treatments can help alleviate itching and discomfort.
Nutritional Support: A healthy diet, rich in fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins, supports liver function and overall health. In some cases, dietary modifications may be recommended to reduce the burden on the liver.
Monitoring and Follow-Up: Regular monitoring through blood tests and imaging studies is essential to assess liver function, monitor bilirubin levels, and evaluate treatment effectiveness. This helps healthcare providers adjust treatment plans as needed and address any complications promptly.