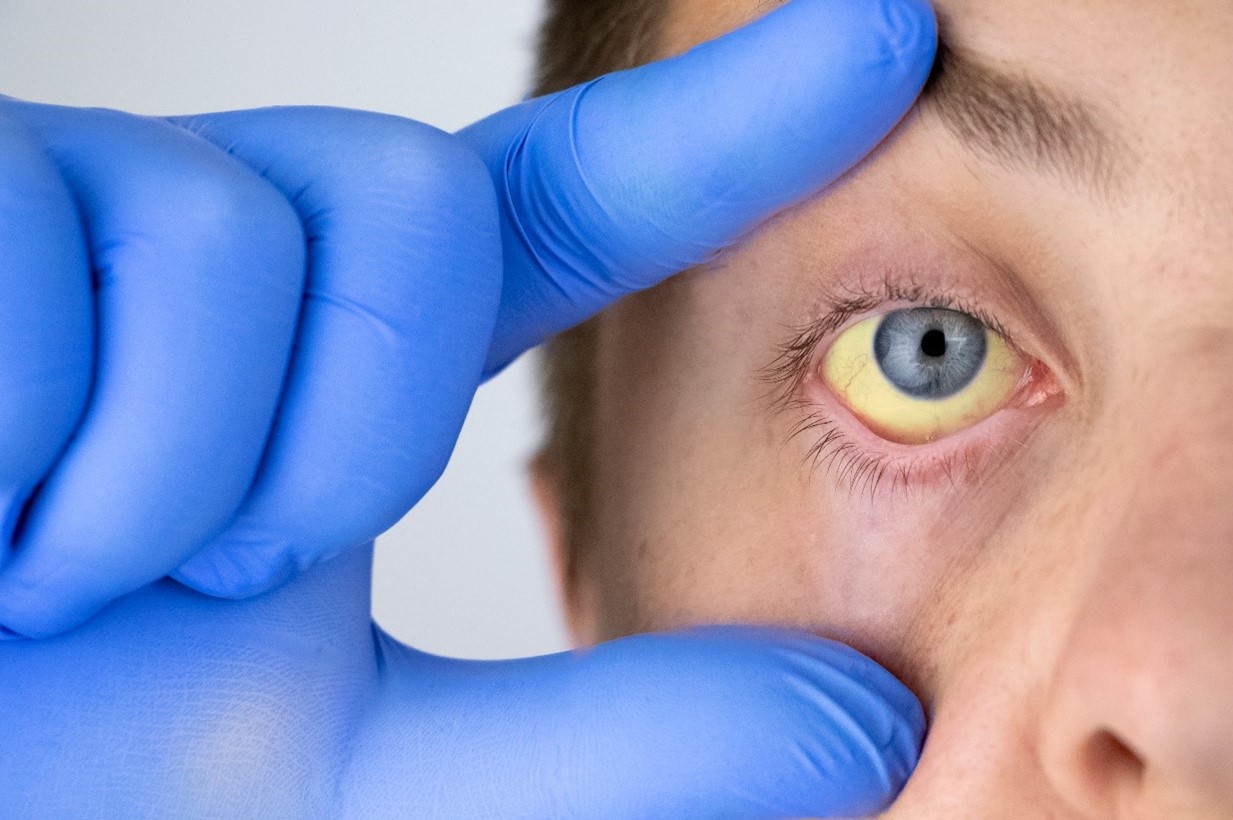
A condition marked by a yellowish tint to the skin, mucous membranes, and the whites of the eyes (sclera). These yellowing signals an issue with the liver or bile ducts, often indicating that the liver is struggling to process bilirubin, a waste product from the breakdown of red blood cells. When the liver cannot effectively filter bilirubin, it accumulates in the blood, leading to jaundice. While jaundice can affect people of all ages, it is particularly common in newborns and older adults.
Causes and Risk Factors
Jaundice occurs when bilirubin processing is impaired. This can result from several factors, including:
- Side effects of certain medications
- Gallstone disease
- Excessive alcohol consumption
- Gallbladder or pancreatic cancer
- Cirrhosis
- Hepatitis or other liver infections
- Hemolytic anemia
In newborns, jaundice is often due to the liver’s underdevelopment, which makes it less efficient at filtering bilirubin.
Symptoms and Complications
Common symptoms of jaundice include:
- Yellowish tint to the skin, eyes, and mucous membranes
- Pale stools
- Dark urine
- Itchiness
- Fatigue, abdominal pain, weight loss, vomiting, and fever
In severe cases, particularly in infants, high bilirubin levels can lead to kernicterus, a form of brain damage.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosing jaundice involves a physical examination and lab tests such as bilirubin levels, complete blood count (CBC), and hepatitis screening. Imaging tests like MRI, CT scans, and ultrasounds, along with liver biopsies, may also be used to determine the underlying cause.
Treatment for jaundice depends on its cause:
- Medications can alleviate symptoms like itching.
- Surgery might be necessary in cases of cirrhosis, cholestasis, or liver failure. Procedures include:
- TIPS (Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt) to reduce portal vein pressure.
- Cholecystectomy is to remove the gallbladder, especially if gallstones or tumors are present.
- Liver transplantation for severe liver failure.
In newborns, treatment options may include phototherapy or blood transfusions to manage high bilirubin levels.
Prevention
Maintaining liver health is key to preventing jaundice. This includes:
- Eating a balanced diet
- Regular exercise
- Limiting alcohol intake
- Avoiding toxins and managing medications carefully
- Avoid smoking, alcohol, and intravenous drugs
- Getting vaccinated before traveling
Jaundice reflects an underlying issue with the liver’s ability to process bilirubin, often due to liver infections, alcohol abuse, or certain medications. Though common in newborns, jaundice can affect anyone. Stay informed by consulting with your doctor about jaundice symptoms and treatments.