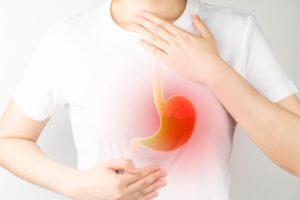
GERD, or gastroesophageal reflux disease, is a digestive condition where stomach contents flow backward into the esophagus, causing irritation. Normally, food travels from the mouth to the stomach through the food pipe. When GERD occurs, this process is disrupted, leading to symptoms such as heartburn and regurgitation of sour liquids into the throat.
Symptoms
- A burning sensation in the chest (heartburn), typically worse at night or when lying down
- Regurgitation of food or sour liquids into the throat
- Upper abdominal or chest pain
- Difficulty swallowing (dysphagia)
- Feeling of a lump in the throat
Causes
- GERD is primarily caused by frequent acid reflux from the stomach. Normally, a circular muscle band at the bottom of the esophagus (lower esophageal sphincter or LES) relaxes to allow food and liquids into the stomach, then closes to prevent reflux. If the LES relaxes abnormally or weakens, stomach acid can flow back into the esophagus, irritating its lining.
Risk Factors
- Obesity
- Hiatal hernia (bulging of the stomach)
- Pregnancy
- Delayed stomach emptying
- Certain medications (e.g., aspirin)
- Smoking
- Consuming large meals or heavy foods late at night
- Excessive alcohol consumption
Diagnosis
- Upper endoscopy to examine the esophagus for inflammation
- Ambulatory acid (pH) probe test to monitor acid reflux patterns
- X-ray of the upper digestive system to visualize the esophagus and stomach
- Esophageal manometry to measure muscle contractions during swallowing
- Transnasal esophagoscopy to inspect the esophagus for damage
Treatment
- Medications to neutralize stomach acid and acid production, Surgical options like Fundoplication to tighten the LES, LINX device (magnetic beads) to prevent acid reflux, transoral incisionless fundoplication (TIF) to strengthen the LES
Lifestyle Modifications
- Maintain a healthy weight
- Quit smoking
- Elevate the head of the bed while sleeping
- Sleep on the left side
- Eat slowly and chew thoroughly
- Avoid trigger foods and beverages like alcohol, caffeine, and fatty foods
GERD is a digestive condition where stomach acid refluxes into the esophagus, causing discomfort like heartburn and regurgitation. Management includes lifestyle changes, medications, and sometimes surgery to alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life. Consistent adherence to treatment and preventive measures is essential for effective management of GERD and minimizing its impact on daily life.