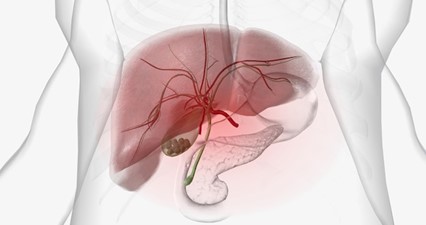
A condition affecting the gallbladder, a small organ located beneath the liver. These hardened deposits can vary in size and composition, posing significant health risks if left untreated.
Here is an overview of gallstones, including their causes, symptoms, and treatment options.
What are Gallstones?
Gallstones are solid formations, develops in the gallbladder due to an imbalance in the components of bile, a digestive fluid synthesized by the liver.
Types:
- Cholesterol Stones: These form from hardened cholesterol due to imbalances in bile composition.
- Pigment Stones: Less common, these consist of bilirubin from the breakdown of red blood cells, often seenin conditions like cirrhosis or sickle cell anaemia.
Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors contribute to the development of gallstones:
- Obesity
- Rapid Weight Loss
- Pregnancy
- Family history
- Gallstones are common in women and older adults.
- Medical Conditions like diabetes and liver disease increase the risk
Symptoms
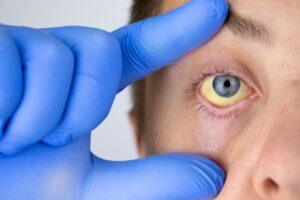
Gallstone symptoms include upper right abdominal pain, especially after fatty meals, along with nausea, vomiting, indigestion, and bloating. Severe cases can lead to jaundice, characterized by yellowing of the skin and eyes due to bile duct blockage. Recognizing signs is vital for early diagnosis and effective treatment of gallstone-related issues.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Gallstones are diagnosed using imaging tests like ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI to visualize the gallbladder and confirm the presence of stones.
Treatment options depend on symptom severity:
- Watchful Waiting: Asymptomatic gallstones may be monitored regularly without immediate treatment.
- Medications are prescribed to dissolve cholesterol stones.
- Laparoscopic cholecystectomy, which removes the gallbladder, is the most common treatment for symptomatic gallstones, offering a safe and quick recovery.
- Endoscopic Procedures: If surgery is not an option, endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) can remove stones from the bile ducts.
Prevention
- Maintain a balanced diet and healthy weight
- Avoid rapid weight loss programs
- Stay hydrated and limit alcohol consumption
Gallstones are diagnosed through imaging tests, with treatment options varying based on symptoms. Options include monitoring asymptomatic cases, using medications to dissolve stones, and recommending surgery such as laparoscopic cholecystectomy for symptomatic relief. Endoscopic procedures are considered when surgery is not feasible. Early diagnosis and appropriate management are important for alleviating symptoms and preventing complications, emphasizing the importance of regular medical check-ups and adopting a healthy lifestyle.